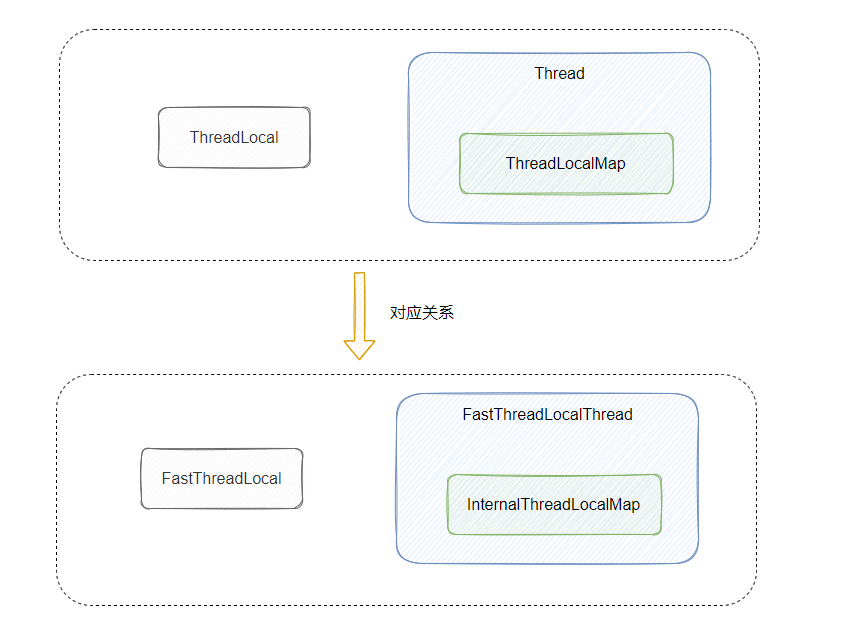
FastThreadLocal
对别
JDK
Netty
Thread
FastThreadLocalThread
ThreadLocal
FastThreadLocal
ThreadLocalMap
InternalThreadLocalMap
区别
区别
ThreadLocal
FastThreadLocal
存储结构
Map<WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>,Object>>
Object[] 数组下标作为索引, Object 存储Value
内存占用
重复对象可以进行覆盖
每次创建会新建下标,不会利用被删除的位置,数组只会扩容,无法缩容
性能
可能产生hash碰撞,线性探测法在解决 Hash 冲突时需要不停地向下寻找,效率较低
定位数据的时候可以直接根据数组下标 index 获取,时间复杂度 O(1)
回收
手动调用Remove 进行回收
1. 自动,执行一个被FastThreadLocalRunnable wrap的Runnable任务,在任务执行完毕后会自动进行FastThreadLocal的清理
源码分析
构造方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public class FastThreadLocal<V> { // FastThreadLocal中的index是记录了该它维护的数据应该存储的位置 // InternalThreadLocalMap数组中的下标, 它是在构造函数中确定的 private final int index; public InternalThreadLocal() { index = InternalThreadLocalMap.nextVariableIndex(); } // 省略其他代码 }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public final class InternalThreadLocalMap extends UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap { // 自增索引, ⽤于计算下次存储到Object数组中的位置 private static final AtomicInteger nextIndex = new AtomicInteger(); private static final int ARRAY_LIST_CAPACITY_MAX_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; public static int nextVariableIndex() { int index = nextIndex.getAndIncrement(); if (index >= ARRAY_LIST_CAPACITY_MAX_SIZE || index < 0) { nextIndex.set(ARRAY_LIST_CAPACITY_MAX_SIZE); throw new IllegalStateException("too many thread-local indexed variables"); } return index; } // 省略其他代码 }
上面这两段代码在Netty FastThreadLocal介绍中已经讲解过,这边就不再重复介绍了。
get 方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class FastThreadLocal<V> { // FastThreadLocal中的index是记录了该它维护的数据应该存储的位置 private final int index; public final V get() { // 获取当前线程的InternalThreadLocalMap InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = InternalThreadLocalMap.get(); // 根据当前线程的index从InternalThreadLocalMap中获取其绑定的数据 Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(index); // 如果获取当前线程绑定的数据不为缺省值UNSET,则直接返回;否则进行初始化 if (v != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) { return (V) v; } return initialize(threadLocalMap); } // 省略其他代码 }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 public final class InternalThreadLocalMap extends UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap { private static final int INDEXED_VARIABLE_TABLE_INITIAL_SIZE = 32; // 未赋值的Object变量(缺省值),当⼀个与线程绑定的值被删除之后,会被设置为UNSET public static final Object UNSET = new Object(); // 存储绑定到当前线程的数据的数组 private Object[] indexedVariables; // slowThreadLocalMap为JDK ThreadLocal存储InternalThreadLocalMap private static final ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap> slowThreadLocalMap = new ThreadLocal<InternalThreadLocalMap>(); // 从绑定到当前线程的数据的数组中取出index位置的元素 public Object indexedVariable(int index) { Object[] lookup = indexedVariables; return index < lookup.length? lookup[index] : UNSET; } public static InternalThreadLocalMap get() { Thread thread = Thread.currentThread(); // 判断当前线程是否是FastThreadLocalThread类型 if (thread instanceof FastThreadLocalThread) { return fastGet((FastThreadLocalThread) thread); } else { return slowGet(); } } private static InternalThreadLocalMap fastGet(FastThreadLocalThread thread) { // 直接获取当前线程的InternalThreadLocalMap InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = thread.threadLocalMap(); // 如果当前线程的InternalThreadLocalMap还未创建,则创建并赋值 if (threadLocalMap == null) { thread.setThreadLocalMap(threadLocalMap = new InternalThreadLocalMap()); } return threadLocalMap; } private static InternalThreadLocalMap slowGet() { // 使用JDK ThreadLocal获取InternalThreadLocalMap InternalThreadLocalMap ret = slowThreadLocalMap.get(); if (ret == null) { ret = new InternalThreadLocalMap(); slowThreadLocalMap.set(ret); } return ret; } private InternalThreadLocalMap() { indexedVariables = newIndexedVariableTable(); } // 初始化一个32位长度的Object数组,并将其元素全部设置为缺省值UNSET private static Object[] newIndexedVariableTable() { Object[] array = new Object[INDEXED_VARIABLE_TABLE_INITIAL_SIZE]; Arrays.fill(array, UNSET); return array; } // 省略其他代码 }
源码中 **get() ** 方法主要分为下面3个步骤处理:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 通过InternalThreadLocalMap.get()方法获取当前线程的InternalThreadLocalMap。 根据当前线程的index 从InternalThreadLocalMap中获取其绑定的数据。 如果不是缺省值UNSET,直接返回;如果是缺省值,则执行initialize方法进行初始化。
下面我们继续分析一下
InternalThreadLocalMap.get() 方法的实现逻辑。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 首先判断当前线程是否是FastThreadLocalThread类型,如果是FastThreadLocalThread 类型则直接使用fastGet方法获取InternalThreadLocalMap,如果不是FastThreadLocalThread类型则使用slowGet方法获取InternalThreadLocalMap兜底处理。 兜底处理中的slowGet方法会退化成JDK原生的ThreadLocal获取InternalThreadLocalMap。 获取InternalThreadLocalMap时,如果为null,则会直接创建一个InternalThreadLocalMap返回。其创建过过程中初始化一个32位长度的Object数组,并将其元素全部设置为缺省值UNSET。
set 方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 public class FastThreadLocal<V> { // FastThreadLocal初始化时variablesToRemoveIndex被赋值为0 private static final int variablesToRemoveIndex = InternalThreadLocalMap.nextVariableIndex(); public final void set(V value) { // 判断value值是否是未赋值的Object变量(缺省值) if (value != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) { // 获取当前线程对应的InternalThreadLocalMap InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = InternalThreadLocalMap.get(); // 将InternalThreadLocalMap中数据替换为新的value // 并将FastThreadLocal对象保存到待清理的Set中 setKnownNotUnset(threadLocalMap, value); } else { remove(); } } private void setKnownNotUnset(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap, V value) { // 将InternalThreadLocalMap中数据替换为新的value if (threadLocalMap.setIndexedVariable(index, value)) { // 并将当前的FastThreadLocal对象保存到待清理的Set中 addToVariablesToRemove(threadLocalMap, this); } } private static void addToVariablesToRemove(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap, FastThreadLocal<?> variable) { // 取下标index为0的数据,用于存储待清理的FastThreadLocal对象Set集合中 Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(variablesToRemoveIndex); Set<FastThreadLocal<?>> variablesToRemove; if (v == InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET || v == null) { // 下标index为0的数据为空,则创建FastThreadLocal对象Set集合 variablesToRemove = Collections.newSetFromMap(new IdentityHashMap<FastThreadLocal<?>, Boolean>()); // 将InternalThreadLocalMap中下标为0的数据,设置成FastThreadLocal对象Set集合 threadLocalMap.setIndexedVariable(variablesToRemoveIndex, variablesToRemove); } else { variablesToRemove = (Set<FastThreadLocal<?>>) v; } // 将FastThreadLocal对象保存到待清理的Set中 variablesToRemove.add(variable); } // 省略其他代码 }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 public final class InternalThreadLocalMap extends UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap { // 未赋值的Object变量(缺省值),当⼀个与线程绑定的值被删除之后,会被设置为UNSET public static final Object UNSET = new Object(); // 存储绑定到当前线程的数据的数组 private Object[] indexedVariables; // 绑定到当前线程的数据的数组能再次采用x2扩容的最大量 private static final int ARRAY_LIST_CAPACITY_EXPAND_THRESHOLD = 1 << 30; private static final int ARRAY_LIST_CAPACITY_MAX_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; // 将InternalThreadLocalMap中数据替换为新的value public boolean setIndexedVariable(int index, Object value) { Object[] lookup = indexedVariables; if (index < lookup.length) { Object oldValue = lookup[index]; // 直接将数组 index 位置设置为 value,时间复杂度为 O(1) lookup[index] = value; return oldValue == UNSET; } else { // 绑定到当前线程的数据的数组需要扩容,则扩容数组并数组设置新value expandIndexedVariableTableAndSet(index, value); return true; } } private void expandIndexedVariableTableAndSet(int index, Object value) { Object[] oldArray = indexedVariables; final int oldCapacity = oldArray.length; int newCapacity; // 判断可进行x2方式进行扩容 if (index < ARRAY_LIST_CAPACITY_EXPAND_THRESHOLD) { newCapacity = index; // 位操作,提升扩容效率 newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 1; newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 2; newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 4; newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 8; newCapacity |= newCapacity >>> 16; newCapacity ++; } else { // 不支持x2方式扩容,则设置绑定到当前线程的数据的数组容量为最大值 newCapacity = ARRAY_LIST_CAPACITY_MAX_SIZE; } // 按扩容后的大小创建新数组,并将老数组数据copy到新数组 Object[] newArray = Arrays.copyOf(oldArray, newCapacity); // 新数组扩容后的部分赋UNSET缺省值 Arrays.fill(newArray, oldCapacity, newArray.length, UNSET); // 新数组的index位置替换成新的value newArray[index] = value; // 绑定到当前线程的数据的数组用新数组替换 indexedVariables = newArray; } // 省略其他代码 }
源码中 set() 方法主要分为下面3个步骤处理:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 判断value是否是缺省值UNSET,如果value不等于缺省值,则会通过InternalThreadLocalMap.get()方法获取当前线程的InternalThreadLocalMap,具体实现get()方法已做讲解。 通过FastThreadLocal中的setKnownNotUnset()方法将InternalThreadLocalMap中数据替换为新的value,并将当前的FastThreadLocal对象保存到待清理的Set中。 如果等于缺省值UNSET或null(else的逻辑),会调用remove()方法,remove()具体见后面的代码分析。
接下来我们看下
InternalThreadLocalMap.setIndexedVariable 方法的实现逻辑。判断index是否超出存储绑定到当前线程的数据的数组indexedVariables的长度,如果没有超出,则获取index位置的数据,并将该数组index位置数据设置新value。
如果超出了,绑定到当前线程的数据的数组需要扩容,则扩容该数组并将它index位置的数据设置新value。
扩容数组以index 为基准进行扩容,将数组扩容后的容量向上取整为 2 的次幂。然后将原数组内容拷贝到新的数组中,空余部分填充缺省值UNSET,最终把新数组赋值给 indexedVariables。
下面我们再继续看下
FastThreadLocal.addToVariablesToRemove 方法的实现逻辑。1.取下标index为0的数据(用于存储待清理的FastThreadLocal对象Set集合中),如果该数据是缺省值UNSET或null,则会创建FastThreadLocal对象Set集合,并将该Set集合填充到下标index为0的数组位置。
2.如果该数据不是缺省值UNSET,说明Set集合已金被填充,直接强转获取该Set集合。
3.最后将FastThreadLocal对象保存到待清理的Set集合中。
remove、removeAll方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 public class FastThreadLocal<V> { // FastThreadLocal初始化时variablesToRemoveIndex被赋值为0 private static final int variablesToRemoveIndex = InternalThreadLocalMap.nextVariableIndex(); public final void remove() { // 获取当前线程的InternalThreadLocalMap // 删除当前的FastThreadLocal对象及其维护的数据 remove(InternalThreadLocalMap.getIfSet()); } public final void remove(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap) { if (threadLocalMap == null) { return; } // 根据当前线程的index,并将该数组下标index位置对应的值设置为缺省值UNSET Object v = threadLocalMap.removeIndexedVariable(index); // 存储待清理的FastThreadLocal对象Set集合中删除当前FastThreadLocal对象 removeFromVariablesToRemove(threadLocalMap, this); if (v != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) { try { // 空方法,用户可以继承实现 onRemoval((V) v); } catch (Exception e) { PlatformDependent.throwException(e); } } } public static void removeAll() { InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = InternalThreadLocalMap.getIfSet(); if (threadLocalMap == null) { return; } try { // 取下标index为0的数据,用于存储待清理的FastThreadLocal对象Set集合中 Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(variablesToRemoveIndex); if (v != null && v != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Set<FastThreadLocal<?>> variablesToRemove = (Set<FastThreadLocal<?>>) v; // 遍历所有的FastThreadLocal对象并删除它们以及它们维护的数据 FastThreadLocal<?>[] variablesToRemoveArray = variablesToRemove.toArray(new FastThreadLocal[0]); for (FastThreadLocal<?> tlv: variablesToRemoveArray) { tlv.remove(threadLocalMap); } } } finally { // 删除InternalThreadLocalMap中threadLocalMap和slowThreadLocalMap数据 InternalThreadLocalMap.remove(); } } private static void removeFromVariablesToRemove( InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap, FastThreadLocal<?> variable) { // 取下标index为0的数据,用于存储待清理的FastThreadLocal对象Set集合中 Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(variablesToRemoveIndex); if (v == InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET || v == null) { return; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") // 存储待清理的FastThreadLocal对象Set集合中删除该FastThreadLocal对象 Set<FastThreadLocal<?>> variablesToRemove = (Set<FastThreadLocal<?>>) v; variablesToRemove.remove(variable); } // 省略其他代码 }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public final class InternalThreadLocalMap extends UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap { // 根据当前线程获取InternalThreadLocalMap public static InternalThreadLocalMap getIfSet() { Thread thread = Thread.currentThread(); if (thread instanceof FastThreadLocalThread) { return ((FastThreadLocalThread) thread).threadLocalMap(); } return slowThreadLocalMap.get(); } // 数组下标index位置对应的值设置为缺省值UNSET public Object removeIndexedVariable(int index) { Object[] lookup = indexedVariables; if (index < lookup.length) { Object v = lookup[index]; lookup[index] = UNSET; return v; } else { return UNSET; } } // 删除threadLocalMap和slowThreadLocalMap数据 public static void remove() { Thread thread = Thread.currentThread(); if (thread instanceof FastThreadLocalThread) { ((FastThreadLocalThread) thread).setThreadLocalMap(null); } else { slowThreadLocalMap.remove(); } } // 省略其他代码 }
源码中 remove() 方法主要分为下面2个步骤处理:
1 2 3 4 通过InternalThreadLocalMap.getIfSet()获取当前线程的InternalThreadLocalMap。具体和3.2小节get()方法里面获取当前线程的InternalThreadLocalMap相似,这里就不再重复介绍了。 删除当前的FastThreadLocal对象及其维护的数据。
源码中 **removeAll() ** 方法主要分为下面3个步骤处理:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 通过InternalThreadLocalMap.getIfSet()获取当前线程的InternalThreadLocalMap。 取下标index为0的数据(用于存储待清理的FastThreadLocal对象Set集合),然后遍历所有的FastThreadLocal对象并删除它们以及它们维护的数据。 最后会将InternalThreadLocalMap本身从线程中移除。
Q&A
为什么 InternalThreadLocalMap 要在数组下标为 0 的位置存放一个 FastThreadLocal 类型的 Set 集合
删除 FastThreadLocal 留扩展接口。
提高 removeAll 的删除效率,不需要去遍历膨胀的数组。
可以更好地做内存泄露的管理